How to Setup Environment Variables Permanently in Ubuntu
Environment Variables are variables used in operating system such as Linux,Windows and Dos to hold global values which can be used by various application process by calling variable names. Environment variables contain information such as disk drive path, or file name. For example, the TEMP environment variable specifies the disk location in which programs place temporary files. Similarly. PATH environment variable specified multiple disk locations where application resides. If application file not found in current directory then Operating Systems search these location for application file.
Apart from these some application set their own variable that they use to perform various operation. Sometime application failed to register environment variable in the Operating System. These post is for those case when you need to setup environment manually.
Ubuntu/Linux store environments variable in /etc/environment file. This file is used for system-wide environment variable settings. This is simple text file consists of assignment expressions, one per line. This file stores the system-wide locale and path settings.
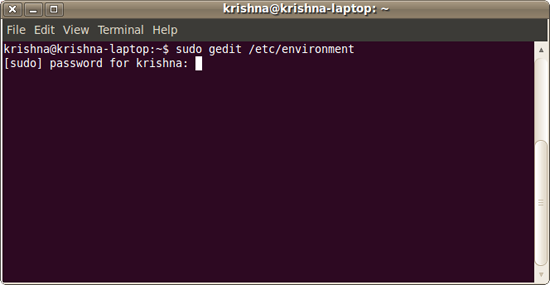
To add environment variable edit this file as super user using gedit or your text editor.
$sudo gedit /etc/environment
Add environment variable and path as specified in next screen shot. Save and exit file. Restart system to load these variables. You can see environment variable values in terminal window. Enter command echo $PATH to see value of environment variable PATH. Make sure to add $ before environment variable name.

Click Here…
How to Setup Environment Variables Permanently in Ubuntu | Bala-Krishna…